Conditions & Treatments
Conditions

Retina Conditions
Age-Related Macular Degeneration
A condition causing vision loss in the central field due to retinal damage, primarily affecting older adults.
Diabetic Retinopathy Screening and Treatment
Routine exams and treatments to prevent and manage retinal damage caused by diabetes.
Vascular Disease
Conditions affecting the blood vessels of the retina, potentially leading to vision problems.
Posterior Uveitis (inflammation)
Inflammation of the back part of the uvea, potentially causing vision loss.
Hydroxychloroquine Retinal Toxicity Screening
Regular eye exams to detect early retinal damage from long-term hydroxychloroquine use.
Retinal Detachment
A serious condition where the retina peels away from its underlying layer, requiring urgent treatment.
Retinal Tears
Small breaks in the retina that can lead to detachment if untreated.
Epiretinal Membrane
A thin layer of scar tissue forming on the retina, potentially causing vision distortion.
Macular Hole
A small break in the macula, causing central vision loss or distortion.
Vitreous Hemorrhage
Bleeding into the vitreous gel of the eye, often causing sudden vision impairment.
Dislocated Intraocular Lenses
Misplacement of implanted lenses, often following cataract surgery, affecting vision.
Hereditary Retinal Disease
Hereditary retinal disease refers to a group of genetic disorders that affect the retina, leading to progressive vision loss.

General Eye Conditions
Cataracts
Clouding of the eye’s lens, leading to vision impairment.
Glaucoma
A condition causing optic nerve damage, often due to increased eye pressure.
Dry Eyes
Insufficient tear production causing discomfort and vision issues.
Blepharitis
Inflammation of the eyelids causing redness, itching, and crusting.
Cornea disease
Conditions affecting the cornea, impairing vision and eye health.
Neuro-ophthalmology
Disorders at the intersection of neurology and ophthalmology affecting vision.
Treatments
Intravitreal Injections
Injecting medication directly into the eye to treat retinal diseases like macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy.
Retinal Laser
Using laser technology to treat retinal conditions such as tears, detachments, and diabetic retinopathy.
Pneumatic Retinopexy
Repairing retinal detachment by injecting a gas bubble into the eye, which presses the retina back into place.
Retinal Surgery eg. Vitrectomy
Removing the vitreous gel to treat retinal detachment, macular holes, or severe bleeding within the eye.
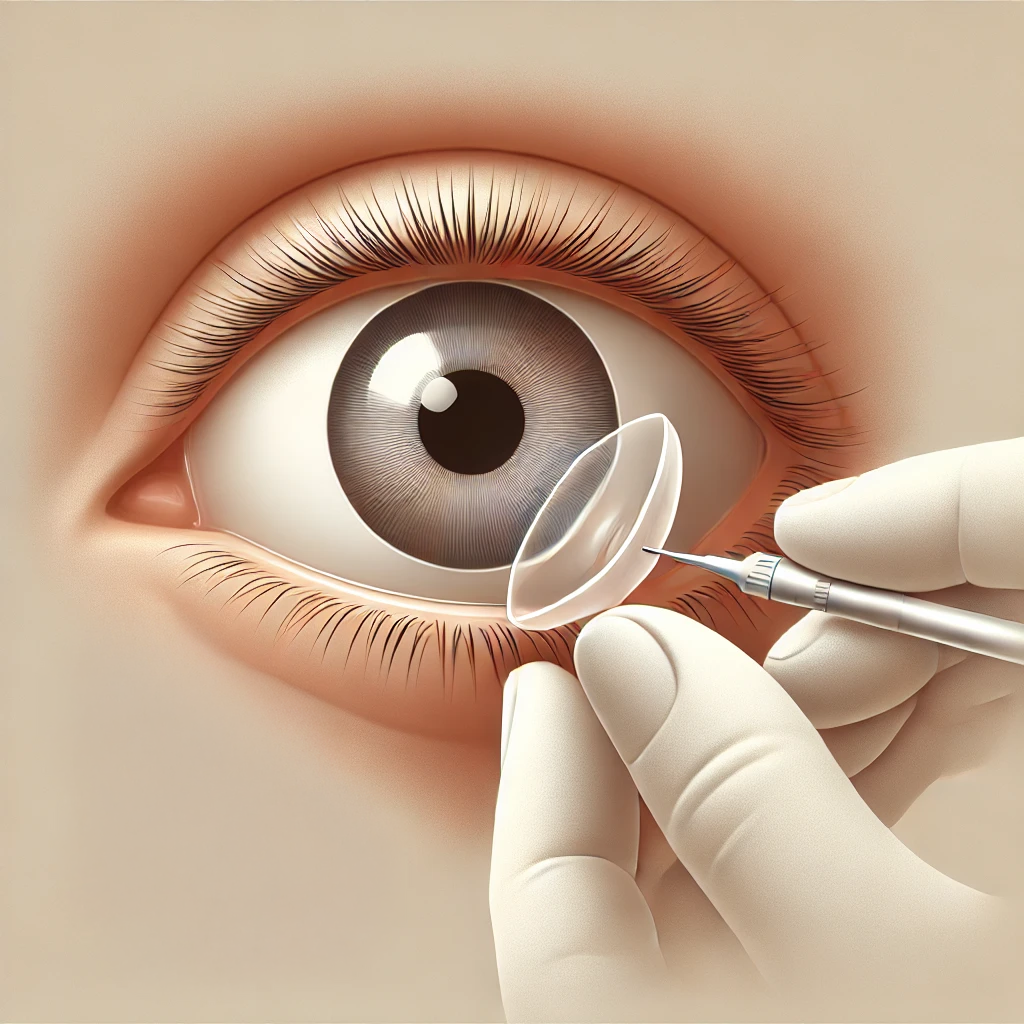
Secondary Intraocular Lenses
Implanting new lenses to replace dislocated or damaged ones from previous cataract surgery.
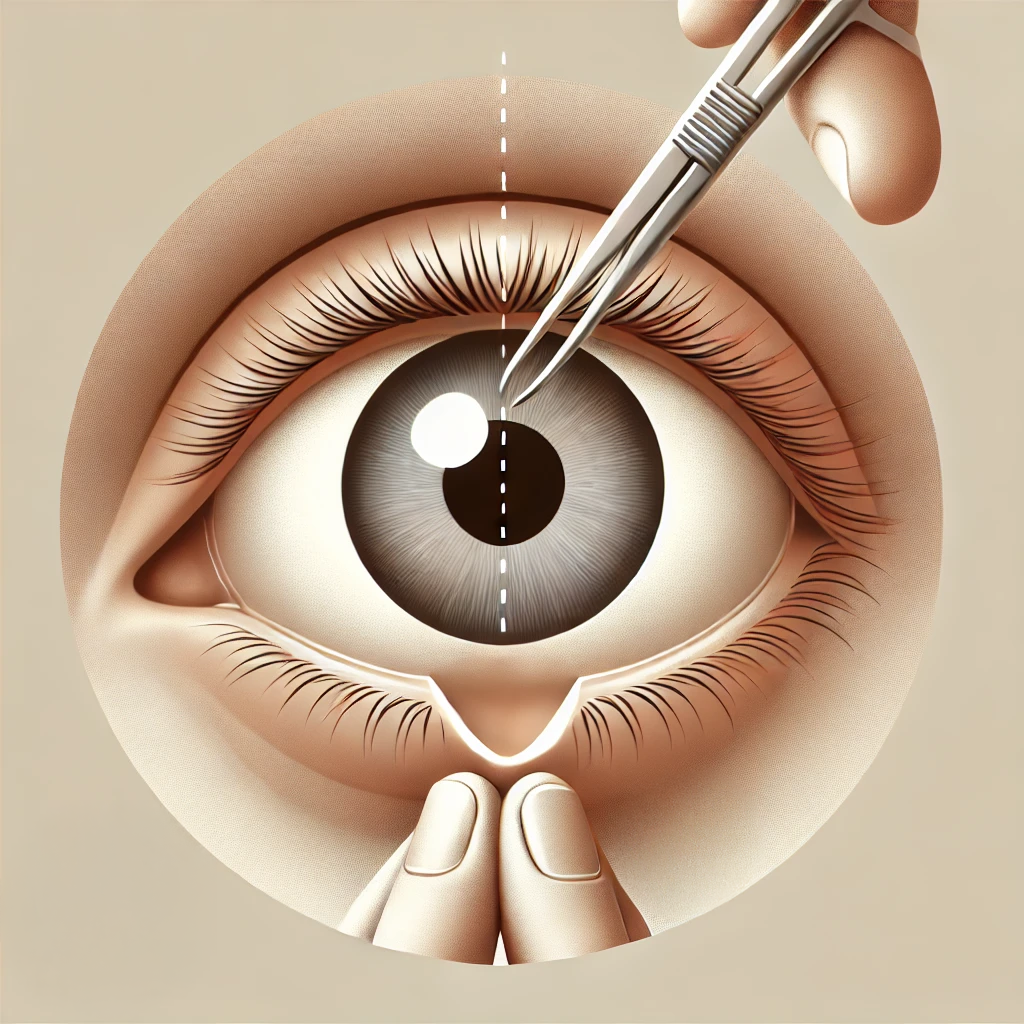
Cataract Surgery
Removing the cloudy lens of the eye and replacing it with an artificial lens to restore clear vision.
Glaucoma Surgery
Procedures to reduce intraocular pressure and prevent further optic nerve damage, preserving vision.
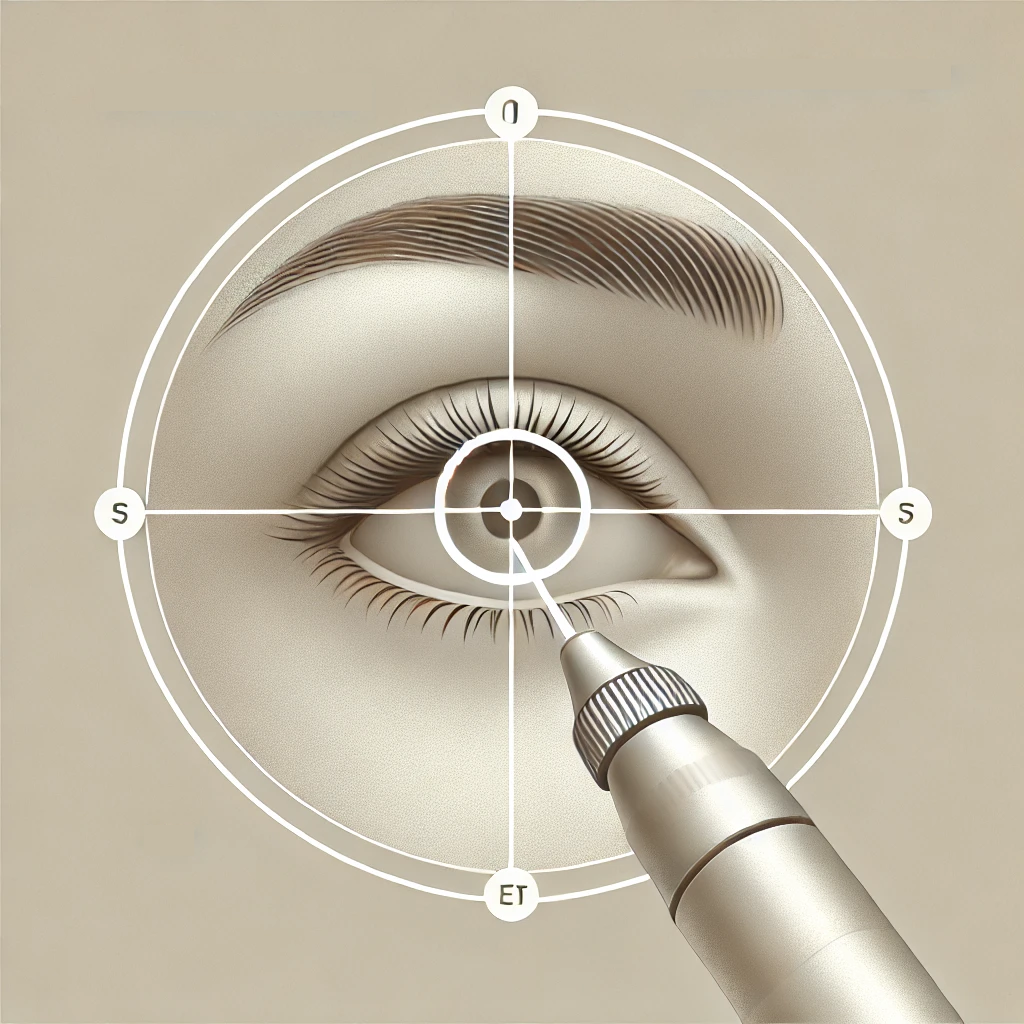
Laser Trabeculoplasty (SLT)
Using a laser to improve fluid drainage from the eye, lowering intraocular pressure in glaucoma patients.

Laser Peripheral Iridotomy
Creating a small hole in the iris with a laser to improve fluid flow and prevent angle-closure glaucoma.
Laser Capsulotomy
Using a laser to clear vision by removing the cloudy membrane that can form after cataract surgery.
Dry Eye Treatment
Various treatments, including artificial tears, prescription medications, and lifestyle changes, to alleviate dry eye symptoms.
